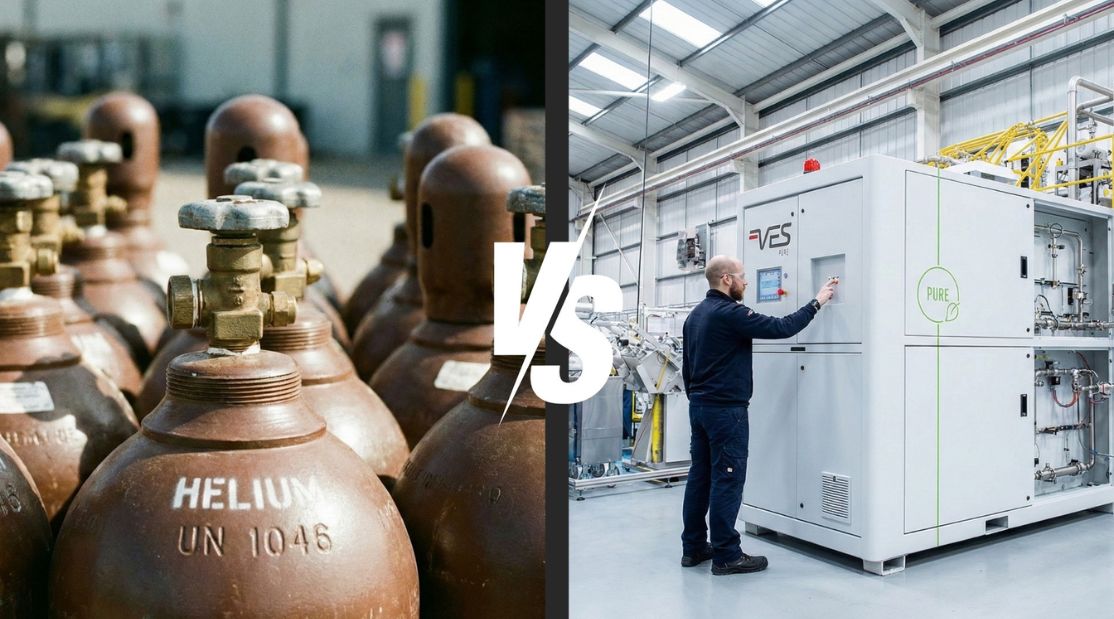
When it comes to leak testing, helium has long been the familiar choice. Its tiny atoms and inert properties make it excellent for detecting even the smallest leaks. But as many engineers have discovered, relying on helium isn’t always straightforward. Prices rise, supply can be unpredictable, and setting up recovery systems often adds layers of complexity.
That’s where argon for leak detection steps in. This often-overlooked noble gas is becoming a serious contender for leak testing, and for good reason.
A Reliable and Capable Option
Like helium, argon is chemically inert, so it won’t react with your systems or materials. Modern detection equipment can now be calibrated to use argon for leak detection effectively, offering results that meet or even exceed stringent testing standards. In industries such as hydrogen pressure vessel manufacturing, inert gases like nitrogen and argon have already been proven to deliver test results equivalent to high-performance helium systems.
Easier to Work With
Argon-based leak testing systems can be simpler to run and maintain. You don’t need bulky recovery banks or complicated mixing stations, which makes the whole setup lighter, quicker to install, and easier to expand in the future. If production volumes increase, argon-based solutions scale well without needing to overhaul your equipment.
This flexibility is especially valuable for engineers managing a wide variety of projects, where speed and adaptability are essential.
Cost Benefits That Add Up
One of argon’s most significant advantages is cost. Helium is scarce, and that scarcity is reflected in its price. Argon, on the other hand, is widely available as a by-product of air separation, making it far more affordable.
To put it into perspective, systems that replace helium with nitrogen have shown cost reductions of more than 98%. Using argon for leak detection offers a similar path to dramatically lower operating costs, without sacrificing capability.
Globally Adaptable
Leak testing equipment must meet strict regional regulations – PED in Europe, ASME in the United States, KGS in South Korea, SELO in China, and so on. Argon-based solutions fit neatly into this framework. With standardised modules and easily interchangeable regulatory components, equipment can be certified, re-purposed, and even relocated worldwide with minimal effort.
Better for the Environment
Sustainability is no longer a nice-to-have; it’s an expectation. Argon’s advantages here are twofold:
- Lower energy use – systems designed around argon can consume up to 30% less power compared to conventional tracer gas setups.
- Reusability – Argon, like nitrogen, can be repurposed after testing to support other factory processes, reducing waste and energy demand.
Unlike helium, which is non-renewable and often released into the atmosphere after use, argon is abundant and readily recyclable.
A Smarter Choice for the Future
For engineers looking to deliver reliable results while keeping costs under control and aligning with sustainability goals, argon is an option well worth considering. It brings together technical performance, ease of use, global compliance, and long-term affordability.
As helium becomes harder to rely on, the option to use argon for leak detection is becoming increasingly realistic, stepping up as a practical and future-ready alternative for leak testing.