Helium leak testing is critical for several components of a heat pump to ensure efficient and safe operation by preventing refrigerant leaks and the primary components that require leak testing are part of the refrigerant circuit, which may use gases like R32, R290 and R410.
These include the compressor, heat exchangers (evaporator and condenser coils), refrigerant piping and tubing, valves, accumulator/receiver and service ports along with any welded or brazed joints.
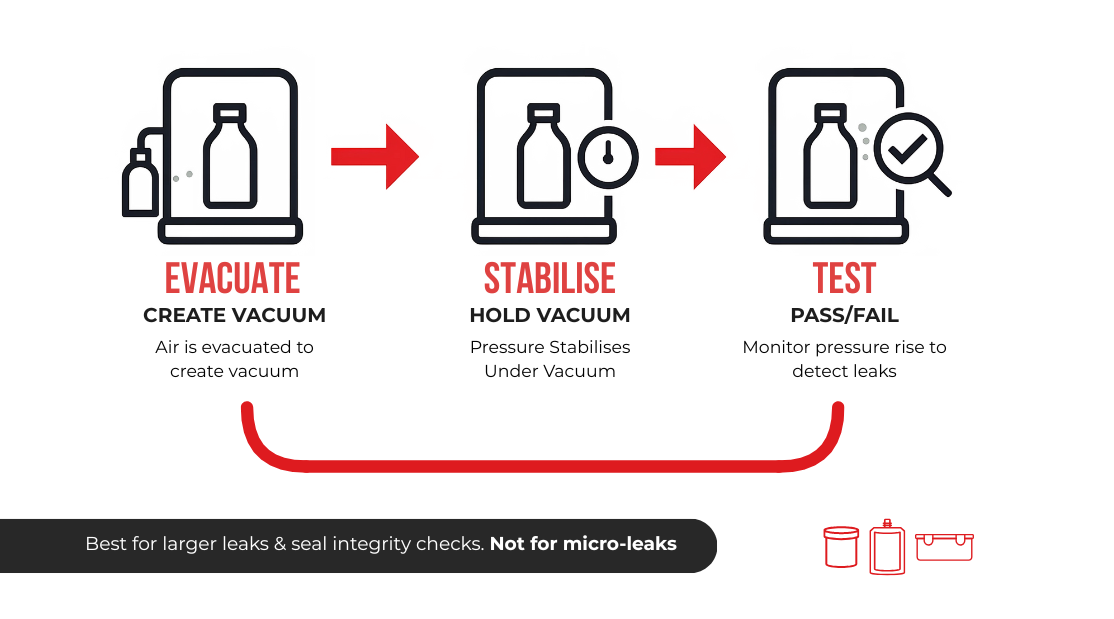
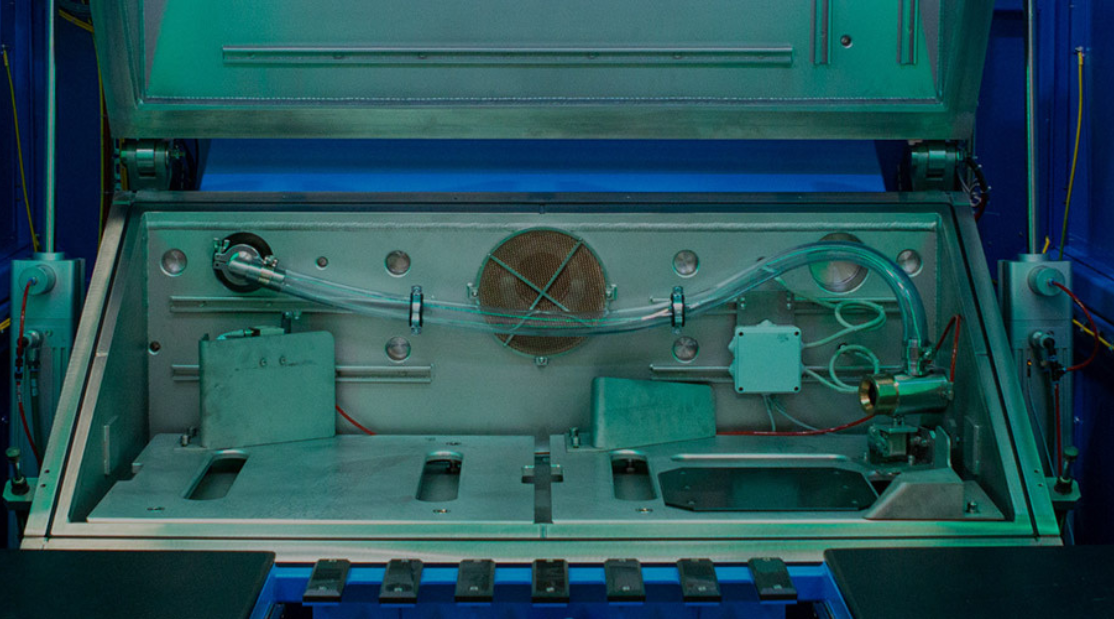
While most heat pump components within the refrigerant circuit can be leak-tested using various methods, hard vacuum chamber leak testing is typically reserved for individual components during the manufacturing process, before final assembly.
This method is particularly effective for ensuring the initial integrity of critical parts.
So, why hard vacuum chamber leak testing?
- High Sensitivity: Testing under a hard vacuum allows for the detection of extremely small leaks that might not be apparent with other methods at atmospheric pressure. The pressure difference between the inside of the component and the near-zero pressure in the chamber significantly amplifies any leakage.
- Accurate Leak Rate Measurement: By introducing a tracer gas (usually helium) into the component within the vacuum chamber, highly sensitive mass spectrometers can precisely measure the rate at which the gas escapes, providing quantitative data on the leak size.
- Quality Control in Manufacturing: This method serves as a rigorous quality control step to identify and reject faulty components early in the production process, preventing defective units from being assembled. Faulty components can be reworked and re-tested to find the exact location of the leak.
With decades of proven performance and capability for safe, reliable and efficient manual, automated and semi-automated hard vacuum leak detection systems please contact our technical sales engineers by email at sales@vac-eng.com